Product Uses Include
Drug discovery target in cardiac research
Measurement of F-actin activated myosin ATPase activity
Identification/characterization of proteins or small molecules that affect myosin II ATPase activity
Identification/characterization of proteins or small molecules that affect the myosin II - F-actin interaction
Control myosin ATPase activity in drug discovery screening projects
Material
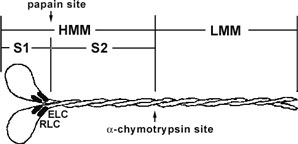
Cardiac myosin protein has been purified from bovine heart muscle. The full length myosin protein has been purified with its essential light chains (ELC) and regulatory light chains (RLC), see Figure 1 and 2. Cardiac myosin has been determined to be biologically active in an F-actin activated ATPase assay, but it is not recommended for use in motility assays because of auto-inhibition (Protease digests with alpha-chymotrypsin and papain may create a subfragment that has F-actin moving properties. Cardiac myosin protein is supplied as a white lyophilized powder. When reconstituted in nanopure water, the protein will be in the following buffer: 100
mM Imidizole pH 7.5, 2.4 M KCl, 0.2 mM DTT, 5% sucrose and 1% dextran. The lyophilized protein is stable at 4°C desiccated (<10% humidity) for 1 year.
Figure 1. Diagrammatic representation of the myosin II protein and its subfragments. Myosin II or conventional myosin is a hexameric protein consisting of two heavy chains and two light chains. Myosin II can be proteolytically cleaved into heavy meromyosin (HMM, Cat.# MH01) and light meromyosin (LMM) by α-chymotrypsin. Heavy meromyosin